Tailored Cellulose Acetate Butyrate (CAB) Solutions for Modern Industry
Structural Features
CAB is derived by partially substituting the hydroxyl groups of cellulose with acetate and butyrate groups. This modification enhances its solubility, flexibility, film-forming ability, and resistance to environmental stress.
Key structural variables include:
- High butyrate content → More flexibility and improved outdoor resistance.
- High acetate content → Harder films and faster drying.
- High viscosity → Ability to form thicker coatings.
Fujian Hongyan Chemical provides a wide range of CAB grades with different butyrate/acetate ratios and viscosities to meet specific industry requirements.

Selection Criteria
Code structure of CAB is on the table at below:
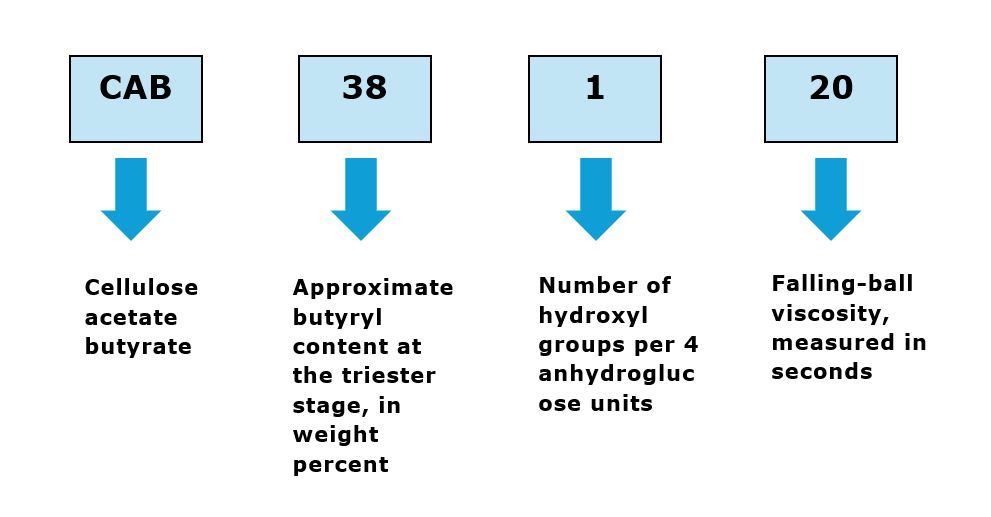
Choosing the right CAB grade depends on several factors:
- Application type: Automotive coatings, plastic finishes, inks, or nail polish require different properties.
- Solvent compatibility: CAB must dissolve well in the selected solvent system.
- Film characteristics: Desired balance of flexibility, hardness, and gloss.
- Processability: Viscosity and drying speed must suit the production process.
For more information, please contact:


Application Areas
Thanks to its versatile structure, CAB is widely used in many industries, including:
- Automotive: Durable, glossy surface coatings.
- Wood and furniture coatings: Transparent, non-yellowing varnishes with UV resistance.
- Cosmetics and nail polish: Glossy, durable, and skin-compatible formulations.
- Printing inks: Fast-drying and scratch-resistant formulas.
- Plastic coatings: Applications that demand clarity and strong adhesion.
- Aerospace coatings: For high-performance, UV-resistant finishes.
- Plastic films & sheet modifiers: Enhances impact resistance and surface properties in blends with PVC, PMMA, or cellulose acetate.
- Cosmetic packaging: Ideal for nail polish bottles and personal care containers due to clarity and chemical resistance.
- Specialty plastics & molding: Used in decorative parts requiring toughness and paint adhesion.
- Protective & barrier coatings: For optical films, labels, and packaging with high chemical resistance.
- Adhesives & sealants: Occasionally used to adjust viscosity and flexibility in solvent-based adhesives.
Typical End Products
- Automotive clear coats.
- Nail polish and nail polish removers.
- Wood lacquers and polyurethane topcoats.
- Flexible inks for packaging (e.g., snack bags).
- High-gloss plastic coatings (e.g., mobile phone shells).
- Outdoor signage and labels.
Advantages
Fujian Hongyan Chemical’s CAB products offer the following key benefits:
- Excellent clarity and gloss level.
- Superior UV and chemical resistance.
- High flexibility and scratch resistance.
- Compatibility with eco-friendly solvents.
- Long shelf life and storage stability.
- Low odor.
- Good pigment dispersion properties.
- Compatible with a wide range of resins and plasticizers.
These features make Fujian Hongyan Chemical’s CAB an ideal choice for formulators seeking both performance and reliability.
CAB in water-based applications
CAB is naturally hydrophobic and insoluble in water. In its raw form, it cannot therefore be used directly in water-based systems.
Solutions for integration into water-based formulations
CAB dispersions
- CAB is dispersed in water using surfactants or emulsifiers.
- Limited solids content (< 30%).
- Requires careful stabilization to prevent sedimentation or phase separation.
CAB emulsions
- Formed by co-solvents or chemical modification.
- Used in special coatings and water-based printing inks.
CAB copolymers and derivatives
- Development of water-dispersible hybrids, e.g., CAB polyurethane.
- Suitable for high-performance coatings with improved properties.
CAB in water-reducible systems
- Combination with water-dilutable resins (e.g., alkyd, acrylic, or urethane resins).
- Use of amines or co-solvents to stabilize the mixture.
Important information – What you should avoid
- Do not dissolve CAB in water in its raw form.
- Do not stir CAB powder directly into water-based systems.
Typical applications in water-based systems
- Primers and clear coats for the automotive industry
- Wood coatings and stains
- Water-based printing inks (e.g. for packaging or textiles)
- Hybrid systems for nail polish top coats
Conclusion
Today, CAB is the ideal solution for manufacturers seeking a balance between technical performance and environmental awareness.
Manufactured according to a quality-oriented production approach, Fujian Hongyan Chemical’s CAB products have established themselves in the industry as reliable and versatile materials. Their technological superiority and adaptability to a wide range of requirements make them a strong partner for future-oriented applications.

Distributed in:
Europe and India, except Spain and UK.
References
- Ma, D., Wasylaschuk, W. R., Beasley, C., Zhao, Z. Z., Harmon, P. A., Ballard, J. M., ... & Reed, R. A. (2004). Identification and quantitation of extractables from cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB) and estimation of their in vivo exposure levels. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis, 35(4), 779-788.
- Nejström, M., Andreasson, B., Sjölund, J., Eivazi, A., Svanedal, I., Edlund, H., & Norgren, M. (2023). On Structural and Molecular Order in Cellulose Acetate Butyrate Films. Polymers, 15(9), 2205.
- Scientific Polymer Products, Inc. – Technical Data on CAB Properties
- https://www.scientificpolymer.com
- Noller, C. R. (1997). Chemistry of Organic Compounds – CAB polymer section.

Gelest Appoints Nordmann as Primary EMEA Distribution Partner

Interview with Timo Diedrichsen




